Get off on the right foot: shedding light on the complex evolution of our “support structures” as bipedal creatures
An extensive international and multidisciplinary research has analysed the evolutionary history of our feet, comparing their complex structure with that of our ancestors, highlighting the relevance of factors such as footwear type and lifestyle, and addressing the complex issue of 'flat feet'
"The human foot is one of the most complex masterpieces of evolution, a work of art in biomechanics: not only it allows us to walk, run and jump, but it is also a true witness of our past and our present", remarks Rita Sorrentino, a researcher at the Department of Biological, Geological and Environmental Sciences at the University of Bologna and first author of an extensive study, published in Communication Biology, shedding new light on the complex evolution of our feet.
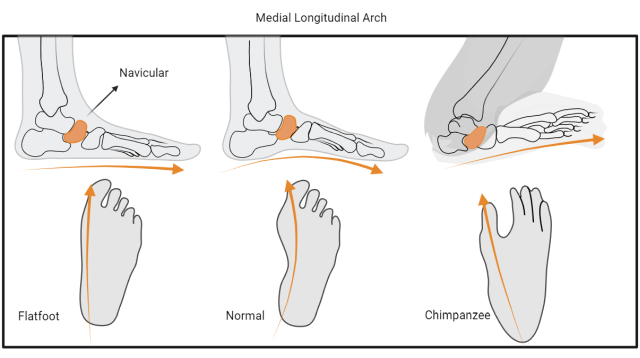
The research activity involving researchers from the Rizzoli Orthopaedic Institute and the University of Pisa focused on the medial longitudinal arch of the foot: a unique characteristic that differentiates our specie - Homo sapiens - from non-human primates.
THE LONGITUDINAL ARCH AND THE FLAT FEET PROBLEM
The longitudinal arch is a functional adaptation that allows the foot to switch from a shock absorber function to lever during the phases of contact and detachment with the ground, a mechanism that allows us to have an efficient bipedal walk. Despite its importance, however, it is still unclear when this characteristic appeared in the course of our evolutionary history. The topic of "flat feet" complicates the picture even more: it is a widespread condition that consists in a more or less pronounced flattening of the medial longitudinal arch.
"Not all flat feet are the same and yet there is not a worldwide clinical definition of flat feet in human beings" explain Alberto Leardini and Claudio Belvedere, scientists from the Laboratory of Movement Analysis and Functional Evaluation of Prosthesis of the Rizzoli Orthopaedic Institute and among the authors of the study.
Scientists have focused in particular on the role of the navicular bone in order to find answers, the keystone of the medial longitudinal arch of the foot.
"The results of this research highlight the variation of navicular morphology among flat-footed people and people with a well-developed longitudinal arch" explains Maria Giovanna Belcastro, professor at the Department of Biological, Geological and Environmental Sciences at the University of Bologna and research coordinator. "More specifically, people who developed flat feet during adulthood show differences concerning the navicular bone shape compared to those with regular arches or with inborn flat feet".
This development raises questions about the nature of inborn flat feet, suggesting that they may represent a normal variant of foot morphology, and thus highlighting the importance of bone morphology in the structure of the foot arch.
FEET AND LIFESTYLE
Scientists also focused on another fascinating topic: differences within modern Homo sapiens population groups. Indeed, the results suggest that the development of the longitudinal arch may be influenced by factors such as the type of footwear, lifestyle and prevailing locomotion strategies.
"We have observed that individuals belonging to hunter-gatherer groups, who live without footwear, show feet that are more flexible in mobility and relatively flatter than those of populations using modern footwear," explains Damiano Marchi, professor at the University of Pisa, one of the discoverers of Homo naledi and one of the coordinators of the study. "These differences may come from different cultural lifestyles and practices: the feet of hunter-gatherer populations could therefore represent a form closer to that of our prehistoric ancestors."
COMPARING FOSSILS
The investigation also compared the structure of our feet with fossils of ancient Homo sapiens and other human species of the past.
"Some of the fossils analysed, such as those of Homo floresiensis, Australopithecus afarensis and Homo naledi, show features in the navicular more similar to those of large non-human primates, suggesting an adaptation to both an arboreal and bipedal lifestyle," explains Stefano Benazzi, professor at the Department of Cultural Heritage at the University of Bologna, one of the study coordinators. "At the same time, the Homo habilis fossils seem to have a configuration more similar to the feet of modern humans, indicating a possible presence of the longitudinal arch; however, this does not exclude the possible presence of a flat foot similar to today's congenital flat feet, given the morphological similarity and proximity of the navicular to that of individuals with a developed longitudinal arch of the foot".
The research ultimately offers a new perspective on the evolution of the human foot and its variability, contributing to our understanding of how this body part has adapted to bipedal locomotion.
Rita Sorrentino, first author of the study explains: "Our foot is a true witness to our past and our present, a fascinating chapter in the great history of human evolution. The results of this investigation provide a comprehensive overview of the morphological variability of the human foot throughout evolution and raise important questions about congenital flat feet, suggesting that they may represent a normal variant of human foot morphology".
THE AUTHORS OF THE STUDY
The study was published on Communications Biology under the title: "Morphological and evolutionary insights into the keystone element of the human foot's medial longitudinal arch." The investigations were conducted by an international, multidisciplinary team consisting of palaeoanthropologists, bioarchaeologists, biomechanical engineers and orthopaedists led by researchers at the University of Bologna from various departments: Biological, Geological and Environmental Sciences (Maria Giovanna Belcastro, Annalisa Pietrobelli, and Rita Sorrentino), Industrial Engineering (Michele Conconi and Nicola Sancisi), Cultural Heritage (Stefano Benazzi and Carla Figus).
Researchers and professionals from the following Universities and Institutes took part in the research: University of Pisa, IRCCS Rizzoli Ortophedic Institute, University of Southern California, University of the Witwatersrand, University of Colorado, Monash University, Collège de France - Paris, Max Planck Institute for Evolutionary Anthropology, Georgian National Museum, Institute for Anthropological Research - Zagreb, University of Southern California, Washington University in St. Louis, New York University, Naturalis Biodiversity Center - Leiden, Western University, The Pennsylvania State University, Dartmouth College.